When you search for something on Google, title tags (or title links) are one of the first things you see. They’re those enticing blue links that tell you what kind of content lives on the page they link to.

Coupled with the website name and your search term, they should give you a clear idea of what you can expect to find by clicking through.
Because title links are so prominent in search results, they’re also an essential part of SEO. And, you guessed it, this makes them harder to optimize and write.
Run through these title tag FAQs to learn everything you need to know to start using them as part of your organic marketing strategy.
Jump to:
- What is a title tag?
- How do you set title tags?
- Are title tags important for SEO?
- How long should title tags be?
- Should I put keywords in title tags?
- Do all my site pages need different title tags?
- How can I check what my title tags are?
- Where do I monitor and review title tags?
- What do title tags do for SEO?
- Should I update my title tags?
- Should I write my own title tags?
- Can I experiment with title tags?
- Can Google change my title tags?
What is a title tag?
A title tag is a one-line description of a web page that is used to label it and enhance it for search engine optimization (SEO).
Title tags show up in 3 important places:
- Link previews (on social media, in emails, messages, etc.), adding locations (like country or city), or adding emojis.
- Address bars (the description in your browser tabs)
- Organic search results (the clickable title that takes you to a website)
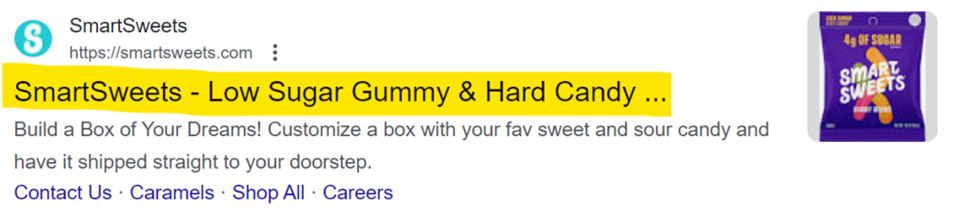
How do you set title tags?
Title tags are set using the HTML tag <title>.
Some SEO tools, like Yoast, can also help you to set, update, and view your title tags.
Are title tags important for SEO?
Yes. Title tags are the first thing that your users see when your content is displayed in organic results. Title tags are a great opportunity to encourage a user to select your content over a competitor’s.
How long should title tags be?
Title tags should be up to 60 characters (or 600 pixels) for the best results.
Should I put keywords in title tags?
Yes, title tags should include keywords.
However, keyword stuffing and keyword cannibalization are just as bad in title tags as they are in body content so choose your keywords wisely and use them strategically.
Do all my site pages need different title tags?
Yes. Each page of your website should have its own, unique title tag. Some may be more straightforward than others (like your about page vs a blog post), but no page should be left without one.
If you don’t set title tags yourself, Google may set them for you.
How can I check what my title tags are?
You can check your title tags using a variety of free tools, such as Moz.
Where do I monitor and review title tags?
You can monitor and review your title tags in Google Search Console.
You can also use a paid tool like SEMrush or Ahrefs.
What do title tags do for SEO?
Title tags describe your page content, which helps both Google and your users.
High-quality title tags can help to increase clickthrough, boost organic ranking, and reduce bounce rate.
Should I update my title tags?
If your title links were never optimized or customized, or you think they could be negatively affecting your site, then yes, you should review and update them.
For larger sites with lots of product pages, you can analyze and update title tags as often as every 3-6 months.
For small sites with few pages, once or twice a year is fine unless you’re running experiments or think your title tags are bringing your traffic down.
Should I write my own title tags?
Maybe. Are you a good writer with some SEO knowledge? Then you can probably give it a shot and see how it goes.
If you struggle with writing (spelling, capitalization, or punctuation) and you aren’t sure where to start with keywords, you can use a free tool like Semrush’s free title generator or hire an SEO specialist to write title links for you instead.
Can I experiment with title tags?
Yes, you can run experiments on title tags. However, you need to make sure that you have numbers from before you make any changes for comparison, and that Google accepts your changes when you make them. Otherwise, it will be hard to tell whether your changes made a difference.
Some experiments include:
- Writing longer or shorter titles
- Swapping keywords around
- Adding locations (like country or city)
- Updating them after a content refresh
Can Google change my title tags?
Yes, Google can change, ignore, and update your title tags at any time. Google wants your title tags to be as relevant as possible to the content they link to, so if the algorithm decides your title link isn’t the best fit, it will generate one of its own.
These title tags are pulled from the page content itself and can fluctuate on a variety of factors, like most things Google.
To have the best shot at having the title link you write show in SERPs, it’s important to:
- Write them with best practices in mind
- Update and review them regularly
- Use keywords relevant to the landing page
- Clearly and concisely describe where they go to
This article was originally written in September 2020. It was last updated in October 2024