
What is a title tag?
Title tags are the unique names of each of your individual web pages. They’re most commonly displayed in SERPs, address bars, and link previews.
The purpose of a title tag is to clearly and concisely describe the content of the web page it references. They can also help with search engine optimization (SEO) because they define the purpose of your page using keywords.
Jump to:
Why are title tags important?
Title tags are important because they’re one of the first things a user sees when your content shows up in search results.
Think about how you determine which search result to click on.
Chances are, you scan the titles (the large, blue links in SERPs) to find the one that best matches the information you’re looking for.
If you come across any that seem too general, too specific, or too unrelated, you’ll skip over them. Until, eventually, you find one that aptly describes the content that matches your query. Then, you click through to the site and, hopefully, get the answer you’re looking for.
Most of your users sort through search results in the same way.
Your title tag is one of your best opportunities to grab a user’s attention and show them you have quality content on your website. If it’s too long, too short, or too confusing, you’ll probably miss out on clickthroughs, regardless of how great your content is and how much time you put into it.
How do I write a title tag?
Title tags are relatively straightforward, but there are some best practices you can keep in mind when writing yours:
1. Stick to a consistent length
Title tags aren’t meant to have unlimited characters. If your title tag is too long, it will be shortened with an ellipsis (…) which can cut out important information. Most SEO experts recommend sticking to a 60-pixel limit, give or take.
If you’re not sure exactly how long your title tag is, you can use a tool like Portent to check it. However, it’s important to note that this tool only displays what your title tag will look like in SERPs, and not in an address bar, which may still be cut off.
2. Make sure you don’t have any typos
Spelling errors and grammar mistakes can be a huge factor in scaring away potential users. If your title tag has a typo in it, it can make your entire website look bad.
Proofread and edit your title tags before you move them live. And, if you’re not sure if they’re correct, have an editor take a look for you.
3. Don’t get keyword stuffy
Keyword stuffing is frowned upon to begin with, but when you are working with character limits, it can be even worse. Don’t get carried away with jamming as many keywords as possible into your title tag. Not only will you risk issues with stuffing, but you could end up cannibalizing your own keywords as well.
Instead, focus on making it descriptive and true to the content of the page.
My best advice? Don’t write for Google, write for your users. Keywords will come naturally.
4. Use a custom favicon
Favicons are the little images that show up in browser tabs next to a title tag. They’re usually branded and feature a logo, company initials, or small graphic.
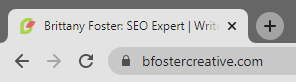
Since these are used in address bars, as bookmark icons, and even in certain link previews, they’re useful for building brand recognition and adding legitimacy to your site.
Without a favicon, Google will show a generic gray globe next to your title tag. While it isn’t the worst thing, it doesn’t help your site to stand out, and it certainly doesn’t do anything for your branding.
5. Analyze and optimize
Each of your web pages should have its own title tag. From your home page to individual product pages, you’re going to need a unique title to describe the content that lives at each URL.
One mistake that people often make is to take a “set it and forget it” approach to title tags. But that just keeps you from finding out what works best for your site and content. Instead, take a look at your title tags every month or so, and after about 3 months, analyze which pages are performing best.
While it won’t always have to do with your title tags, tweaking the titles for underperforming pages could help to give them a boost. Changing simple things like adding a country abbreviation (like US or CA) or swapping in an alternate name can end up making a big difference.
6. Keep up with Google
If you don’t stick to Google’s title tag guidelines, they may select and display one for you. Make sure that’s you’re following best practices and paying attention to algorithm updates so that the titles you work so hard to write are the ones that Google uses.
Check your title tags in SERPs every so often to ensure that Google is displaying the title tag you’ve set. If Google chooses a different page title for you, the best thing to do is to go back and make sure you’re doing everything you should be. Following best practices and making quality, unique title tags is the best way to ensure that they show up properly.
7. Write for your users
The gist of all the best practice articles and posts out there is to write for your users. As with any SEO content, consider reading level, clarity, consistency, and correctness when writing your title tags.
Don’t get carried away with flashy emojis or animations—if they aren’t used properly, all they do is make your site look cheesy and cheap. Plus, Google can choose to filter them out if it decides they aren’t relevant or useful.
Write quality, user-focused content that aligns with the purpose of each page. Sprinkle in keywords when they make sense and provide useful information.
Do I need title tags?
If you have a website that has webpages, then yes, you absolutely do need title tags. If you don’t set title tags yourself, Google will set them for you, but they might not always be correct.
I’ve seen the overwhelmingly positive results that high-quality title tags can have on SEO profits, and they’re absolutely worth customizing. However, when not written properly, they can have little to no effect on clickthrough, so they’re worth doing the right way.





